Introduction
The dramatic increase in the prevalence of obesity and diabetes has become a major public health problem worldwide. Diabetes Mellitus type II (DMT2) is by far the most severe metabolic problem that humanity suffers. In Spain DMT2 affects 10-25% of the population. There are three million diabetics between 30 and 60 years. DMT2 accounts for 90-95% of cases of diabetes.
Morbid obesity (MO) is a pandemic disease that affects 15-30% (depending on the country) of humanity and especially in modern societies and 1.000 million people suffer this chronic diseases with altered metabolic functions and increase mortality. It incidence increases every decade, that today exceeds the population affected by hunger. The increased incidence of obesity is dramatic and global public health problem and demands urgent attention of governments, health care and the medical community. DMT2 should be prevented and provide effective treatment.
Diabetes and obesity(Dia-besity)
It is an accepted term to describe this dual pathology that often accompanies each other and is by far the most severe metabolic problem that humanity suffers and outnumbers those affected by famine. 50% of the population are obese and 20-25% MO.
Epidemiological features of this condition
- 383 million people have DMT2. 438 million in 2030 and 2035, the number will increase to 592 million.
- The number of people with T2DM is increasing in all countries.
- 80% of people with diabetes live in low- and middle-income.
- Most people with diabetes are between 40 and 59 years.
- 175 million people with diabetes are undiagnosed.
- Diabetes causes 5.1 million deaths in 2013: every 6 seconds a person dies due to diabetes
- In 2013, diabetes health spending generated at least 548.000 million, 11% of total expenditure in adults
- More than 79.000 children developed type 1 diabetes in 2013
- More than 21 million mothers of live births were affected by diabetes during pregnancy in 2013
Surgery of obesity began in the 50´s of the last century and has proved very effective in many patients suffering from DMT2 but not is indicated in young patients with type I DM (DMT1), where the pancreatic insulin production is congenitally lacking. DMT2 accounts for 90-95% of cases of diabetes. Only 45% of the populations of European origin, are not overweight. The average HbA1c of the diabetics is 7[1].
Pories[2] wrote in 1995 an article "Who would have said? Obesity surgery is the most effective therapy to treat adult-onset diabetes"
Buchwald [3] and others [4-10] reported the effectiveness of different bariatric techniques in controlling diabetes being restrictive techniques as gastric bands the less effective for cure of 68%, gastric tube >72% , gastric bypass >89% and complex techniques biliary-pancreatic diversion such as Duodenal Switch (DS) and DBP type Scopinaro>97%. Mean remission of diabetes was 78.1%. In our experience with over 950 MO patients the DS of diabetic patients had a 100% cure for their diabetes.
Historic case
A 48 years old, Male patient, BMI-33, diabetic first treated with Glucophage and then insulin therapy of 110 IU, Glucose-285, Cholesterol-224, HDL-34 Triglycerides-262, HA1c-8.5 is referred to us for surgery diabetes for a Laparoscopic DS in January 2004. Co-morbidities: retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy in limbs tingling, extreme pain at 200 meters and his feet were cold all the time and had a complete severe erectile dysfunction. He was referred to us by Dr H. Buchwald, since the patient´s wife, was a patient of him with a previous DS. The final diagnosis was metabolic syndrome.
On 02.19.2004 he has an standard BPD/DS (Biliopancreatic diversion/Duodenal Switch) with a 185 cm Digestive Loop, 250 cm biliopancreatic loop and 65 cm common channel. But gastric resection was not done considering his low BMI. The postoperative course was completely normal and was discharged on the second day in a free diet. He had no serious problem of diarrhea although he had more frequent stools at first.
The pos-op course was completely normal with glucose levels falling within 95 and HBC1 at levels of 5 to 5.5. The postoperative short and long term course is reflected in the writing that sent us his wife, a former scrub nurse of Dr. Michael De Bakey(Figure 1).
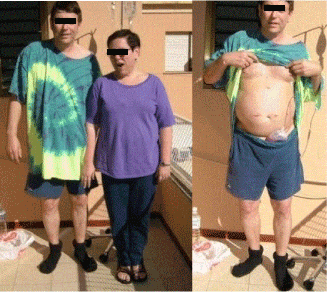
Figure 1. Pre-op with BMI-33
July 8.2004--This is Pat Laird, Dan´s wife and DS patient of Dr. Henry Buchwald. It is kind you write and inquire about Dan. I sent you a patient, Dr. Jim Heeter also from Minnesota. His surgery will be in October and you would like him. My sister Judy Clegg had surgery with you 3 days after Pat and she is doing OK. Now I will answer your questions about Dan = Daniel. He is doing wonderful: a real success story and I think you should be writing a paper. The medical community needs to know this. Dan feels great, looks great, and he is so glad he had the surgery. He has no problems with the diet and has continued exercise. His weight stabilized between 190 and 200 lbs (86 and 91 Kilos). His abdomen is still disproportionately large compared to the rest of his body. His scars are fading well and he had no post-op problems. Here´s what is clinically significant. 1) No longer a diabetic. HA1c normal and he has added sugars and carbohydrates to his diet; 2) Diabetic retinopathy gone and its effects have been reversed. His vision is 20/20 without glasses and his eyes are no more longer red all the time: 3) Diabetic Neuropathy (feet) all that´s left is slight tingling sensation, other than that, it is gone. Before surgery, he complained of severe pain/ discomfort all the time. Post-op he has improved so much that he can walk any reasonable distance. Before surgery he was in extreme pain walking 500 ft. His feet were cold all the time. His circulation has improved dramatically. 4) ED (erectile dysfunction). Dan had been unable since 1998 to perform sexually. He stopped having nocturnal erections as well. He tried Viagra (150 mg the big one) with no success. He had pretty much given up on ever having sex again. 1o or 12 weeks post-op started noticing nocturnal erections and soon after, he was able to have sex again. He´s not the same as when he was 20´s but he´s much grateful now than ever was then. He will never take sex for granted again! The doctors here told him the ED was because diabetes was affecting his circulation and it was permanent. Thank you for the wonderful gift Dr B! Now you know the full story.
Oct 24, 2012 -- Dan died almost a year ago and I thought long and hard before posting this. In the end I decided to go ahead because that's what he would have wanted me to do. I hesitated because I didn't want people to think the DS had anything to do with his death. Dan was thrilled with his surgery and had no regrets. He always said he would do it over again in a heartbeat. The results were exactly what he had hoped for. In short, Dan ended up with the best of both worlds. He could eat as he pleased, including junk foods, and not gain weight. And his diabetes was gone. High protein was no problem because he loved meat. Vitamins’ were no big deal because he was already used to taking every supplement known to man. His labs were always good and just to be honest, Dan ate like a horse! I think he was making up for all the years he did without.
Considerations
The term Metabolic Surgery (MS) is so accepted today that most bariatric societies have included this term to the previous title of each society. MS means any manipulation surgically done to alter metabolism or absorption of food intake. The successful operation of this therapy is represented by the "surgery hypercholesterolemia" developed by Buchwald [11] as ileal exclusion in 1964 with the derivation of the distal third of the intestine and had a remarkable long-term results. Partial ileal exclusion represented a significant, sustained reduction unchanged for over 20 years after the operation [12]. Baltasar[13] published the only three cases performed in Spain. This successful operation was abandoned when the use of cholesterol reducing medicines made it unnecessary.
I have done a survey among Spanish bariatric surgeons by questioning the members of SECO (Spanish bariatric surgery society) on the date of initiation of metabolic surgery in Spain, without any data that it had been used prior to 2009. This is the purpose of this publication.
We have no evidence that the DS without gastrectomy technique has been used previously for diabetes. Marceau [14] describes this technique in an interesting article in 2014 as an alternative to DS in patients who for one reason or another could not make them and compare the DS results on three types of alternatives: a) With a vertical gastrectomy (Sleeve gastrectomy-forming); b) DBP as in the case we presented today and 3) Complete DS. Weight losses are better with the complete DS, second is DS without gastrectomy (as in this case) and finally the SFG has lower weight losses.
References
2021 Copyright OAT. All rights reserv
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2004) Prevalence of overweight and obesity among adults with diagnosed diabetes--United States, 1988-1994 and 1999-2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep53: 1066-1068. [Crossref]
- Pories WJ, Swanson MS, MacDonald KG, Long SB, Morris PG, et al. (1995) Who would have thought it? An operation proves to be the most effective therapy for adult-onset diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg222: 339-350. [Crossref]
- Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, et al. (2004) Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA292: 1724-1737. [Crossref]
- Moo TA, Rubino F (2008) Gastrointestinal surgery as treatment for type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes15: 153-158. [Crossref]
- DePaula AL, Macedo AL, Rassi N, Machado CA, Schraibman V, et al. (2008) Laparoscopic treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus for patients with a body mass index less than 35. Surg Endosc22: 706-716. [Crossref]
- DePaula AL, Macedo AL, Mota BR, Schraibman V (2009) Laparoscopic ileal interposition associated to a diverted sleeve gastrectomy is an effective operation for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with BMI 21-29. Surg Endosc23: 1313-1320. [Crossref]
- Cohen Ricardo, Pinheiro JS, Correa JL, Schiavon CA (2006) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for BMI<35 kg/m2; a tailored approach. Surg Obes Relat Dis2: 401-404. [Crossref]
- Cohen RV, Schiavon CA, Pinheiro JS, Correa JL, Rubino F (2007) Duodenal-jejunal bypass for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in patients with body mass index of 22-34 kg/m2: a report of 2 cases. Surg Obes Relat Dis3: 195-197. [Crossref]
- Baltasar A, Bou R, Bengochea M, Serra C, Pérez N (2006) Mil operaciones bariátricas. Cir Esp 79: 349-355.
- Bou R, Baltasar A, Pérez N, Serra C, Bengochea m, et al. (2012) Cirugía de la Diabetes. Gastrectomía vertical y desvío duodenal. Video. BMI 2: 20-22.
- Buchwald H (1964) Lowering of Cholesterol Absorption and Blood Levels by Ileal Exclusion Experimental Basis and Preliminary Clinical Report. Circulation29: 713-720. [Crossref]
- Buchwald H, Stoller DK, Campos CT, Matts JP, Varco RL (1990) Partial ileal bypass for hypercholesterolemia. 20- to 26-year follow-up of the first 57 consecutive cases. Ann Surg212: 318-329. [Crossref]
- Baltasar A, Marcote E, Bou R, Bengochea M, Arlandis F (1991) Exclusión ileal parcial en la hipercolesterinemia. Cir Esp49: 475-478.
- Marceau P, Biron S, Marceau S, Hould FS, Lebel S, et al. (2014) Biliopancreatic Diversion- Duodenal Switch: Independent Contributions of Sleeve Resection and Duodenal Exclusion. Obes Surg24: 1843-1849. [Crossref]

