Abstract
Background: Find a therapy can block DHEAS also in women who are unable to receive combined estrogen-progestin therapy due to various reasons (e.g., increased risk of thrombosis, and side effects associated with the use of estrogen-progestin)
Objective: The aim of our pilot study was to determine the effects of inositol in the treatment of PCOS patients with acne.
Methods: This was a spontaneous prospective observational pilot study conducted at two Centers in Italy, specialized in the treatment of dermatological diseases
According to a table of randomization, patients were divided into two groups:
Group A
50 patients who had been prescribed:
• 2 grams of inositol, 2 times a day, orally, for six consecutive months.
Group B
50 patients who had been prescribed:
• 200 micrograms of placebo 2 times a day, orally, for six consecutive months.
Randomization been through assignment from a telephone central office independent from the place of trial
Results: In group A, DHEAS blood levels were reduced. In group B, DHEAS blood levels were almost unchanged
Limitations: Further studies with a randomized design are required to either confirm or discard these preliminary findings.
Conclusion: In conclusion, these observations suggest that inositol may be useful as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of female patients with moderate acne, especially in the case of women who are unable to receive combined estrogen-progestin therapy due to various reasons (e.g., increased risk of thrombosis, and side effects associated with the use of estrogen-progestin).
Key words
acne, inositol, hyperandrogenism, PCOS
Summary
Acne, once considered as a mere aesthetic problem, is now recognized as a disease that can cause major disturbances of the psychological and emotional sphere.
Currently, the treatment of acne is focused on one or more pathogenic factors: hormonal stimulation and sebaceous hypersecretion, disorder of keratinization, colonization of Propionibacterium acnes and inflammation [1]. The aim of the Authors is to evaluate the use of inositol in patients with moderate acne and PCOS
Introduction
Acne is a very common condition, which affects approximately 80-90% of adolescents [1]. It occurs predominantly at the face, chest and back, the areas of the body with the highest prevalence of sebaceous glands [2].
Over the last decades, a number of topical and systemic compounds for the treatment of acne have been introduced into the market [2]. Acne therapy aims to correct one or more of the pathogenic factors which underlie the disease: hormonal stimulation and sebaceous hypersecretion, keratinization disorders, colonization by Propionibacterium acnes and inflammation [2]. However, the need for new studies on the efficacy and safety of different treatment has been recently pointed out [2].
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common endocrine causes of acne, often characterized by ovulation disorders such as oligo- or amenorrhea [3]. It has been estimated that 30-40% of women with PCOS present with have impaired glucose tolerance; a defect in the insulin signaling pathway has been linker with the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Therefore, insulin-lowering medications could represent a promising approach in women with PCOS and acne. In particular, the efficacy of inositol for the treatment of moderate-severe acne has been preliminary investigated [3,4], but further evidence appears necessary for a comprehensive evaluation of the efficacy and safety of this therapy.
The aim of our pilot study was to determine the effects of inositol in the treatment of PCOS patients with acne.
Patients and methods
Study setting and design
This was a spontaneous prospective observational pilot study conducted at four Centers in Italy, specialized in the treatment of dermatological diseases. The study was conducted from June 2012 to December 2013.
Patients
Female patients with acne and PCOS, naïve for acne treatment, were eligible to this study. Diagnosis of PCOS was performed on the basis of the clinical picture, hormonal and ultrasound analysis and was confirmed by a gynecologist. More specifically, according to the Rotterdam criteria [5], the diagnosis of PCOS is made when a patient presents at least two of the following alterations: (i) oligoovulation and/or anovulation; (ii) excess androgen activity; (iii) polycystic ovaries [6]. Patients were excluded if they presented concomitant endocrine and metabolic disorders, such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, androgen-secreting tumors, adrenal hyperplasia, and Cushing syndrome. In all patients, venipuncture was performed in order to determine the serum concentration of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEAS). Concomitant medications for the treatment of acne were not allowed.
Study procedures
According to a table of randomization, patients were divided into two groups:
Group A
50 patients who had been prescribed:
• 2 grams of inositol, 2 times a day, orally, for six consecutive months.
Group B
50 patients who had been prescribed:
• 200 micrograms of placebo 2 times a day, orally, for six consecutive months.
Randomization been through assignment from a telephone central office independent from the place of trial
After the discontinuation of therapy, patients were followed-up for three months.
Treatment selection was performed according to clinical judgment. All patients returned for a control visit three months after the initiation of therapy. A further follow-up visit was planned at three months since the termination of therapy (i.e. six months from baseline).
The following variables were assessed, at baseline and after a 3-month therapy: global acne severity scale (GEA); Cardiff Acne Disability Index (CADI); concentration of serum DHEAS. Safety considerations were also performed.
Results
During the study period, patients were randomly divided into two groups, as previously reported.
No significant difference was found between the two groups in terms of average age and BMI.
From a clinical point of view, group A patients showed a marked improvement of the skin (Figure 1and 2).
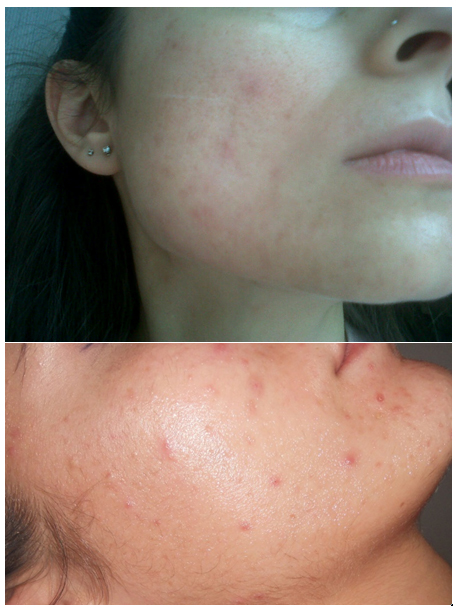
Figure 1.
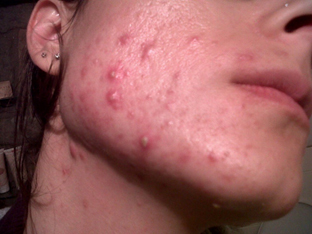
Figure 2. Clinical skin of a patient before (A) and after (B) therapy with placebo.
In particular, papulopustular lesions were reduced and the inflammation was eliminated.
With reference to group B, 2 patients had a mild clinical improvement, and 40 patients showed no improvement.
In group A, DHEAS blood levels were reduced (Table 1).
In group B, DHEAS blood levels were almost unchanged (Table 1).
The severity of acne lesions was evaluated by means of the GEA (Global Evaluation of Acne) clinical scale. The impact of acne on the Quality of Life of patients with acne was assessed by means of the CADI (Cardiff Acne Disability Index) scale. No adverse events were recorded.
All data were analyzed by descriptive statistics. Due to the purely-descriptive nature of the present study, statistical comparisons between baseline and end of treatment or between groups were not performed.
Discussion
Current Guidelines for the treatment of acne have pointed out the importance of a tailored therapy for patients with acne [5,7]. A correct diagnostic approach and the selection of an adequate therapy seem therefore fundamental in order to pursue two main objectives: the resolution of the clinical picture and the prevention of permanent scarring, which may lead to major aesthetic and psychological consequences.
Inositol can play a role to achieve those aims.
The factors that contribute to the formation of acne include androgens and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in particular: this is a derivative of testosterone, which starts to be produced at puberty and is able to develop and activate sebaceous glands. DHT is the main factor, but many others contribute to the pathogenetic mechanism of the disease.
Hyperkeratinization of the infundibulum causes a progressive occlusion of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland, leading to sebum accumulation. The obstruction of the excretory duct induces blackhead formation of a few millimeters (microcomedone) or bigger (macrocomedone), which can be found on the skin surface, with no signs of inflammation. The hormones involved in the regulation of sebaceous glands include dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), androstenedione, testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). In women, adrenal glands are the major source of androgens, although the ovaries are capable of producing testosterone, androstenedione, and dehydroepiandrosterone. Testosterone undergoes two peripheral (or extraglandular) metabolic pathways: one is the peripheral aromatization of estrogen through the action of aromatase, which takes place mainly in the muscle and adipose tissue; the other is the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone by 5α-reductase in the target organs, including the skin [8-11].
The metabolism of androgens in keratinocytes and sebocytes begins with the transformation of DHEA into androstenedione and, then, testosterone, through the action of two cytoplasmic enzymes: the 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase [10].
Dihydrotestosterone synthesized from testosterone by action of the enzyme 5α-reductase is the final and most important product of metabolism involved in the androgenic stimulation of sebaceous secretion [12].
A study showing the therapeutic efficacy of inositol in patients with acne and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) has already been published in literature [13]. The present work is one of the few trials that focus on inositol, part of the vitamin B complex, and on its effects on patients suffering from moderate-to-severe acne and PCOS.
In particular, this present study evaluates the effects of inositol on the skin of acne patients suffering from microcystic ovaries, as well as serum testosterone levels before and after the therapy [3,4,14-16]. Inositol also plays a specific role in the control activity of the metabolism of fats and sugars [14,17,28]. In this context, this molecule may be useful to prevent and correct the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the metabolic alterations linked to acne.
This study shows that, in female patients with moderate acne, inositol treatment improves the clinical condition of skin by reducing hyperandrogenism.
These results are in line with those found in other studies, suggesting a positive effect of inositol in reducing serum concentrations of testosterone [3,14,16,18-28,].
In conclusion, these observations suggest that inositol may be useful as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of female patients with acne, especially in the case of women who are unable to receive combined estrogen-progestin therapy due to various reasons (e.g., increased risk of thrombosis, and side effects associated with the use of estrogen-progestin).
Further studies with a randomized design are required to either confirm or discard these preliminary findings.
Acknowledgements
We thank patients involved in this study and Michela Renna (M.A.) for her language advice and assistance.


