A male adult patient came to the trauma outpatient clinic due to increasing pain and paresthesias beginning at the dorsal side of the left wrist three months ago, in the further time course slowly extending to the elbow. If the patient bended his wrist, these symptoms exacerbated. The clinical examination revealed a 3 x 2 cm tumescence and induration at the dorsal aspect of the wrist. For further exploration of this finding an MR examination of the wrist was requested.
The MR examination showed a fairly demarcated, significantly gadolinium enhancing mass, potentially a benign tumor, encompassing extensor tendons (Figure 1 and 2).
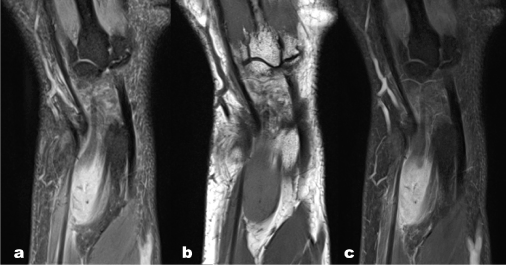
Figure 1. MR examination of the left wrist. a) PD-weighted fat suppressed, b) T1-weighted turbo spin-echo, and c) gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted turbo spin-echo with fat suppression in coronal orientation show a fairly demarcated, significantly gadolinium enhancing soft tissue mass located at the dorsal side of the wrist.
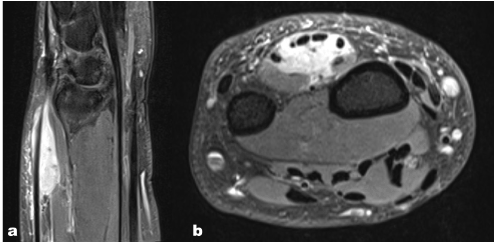
Figure 2. Sagittal PD-weighted fat suppressed (a) and transverse gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted turbo spin-echo with fat suppression demonstrate that the mass surrounds extensor tendons.
After the diagnostic procedures, the mass lesion was excided. Patho-histological workup delivered the final diagnosis of a myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma. Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomas are rare, malignant soft tissue neoplasms with about 200 cases reported in the literature [1], first described by Montgomery in 1998 [2]. They are low-grade malignancies, the incidence of metastases is very low, less than 2% [3].
- Kobayashi E, Kawai A, Endo M, Y, Takeda K, Nakatani F, et al. (2008) Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma. J Orthop Sci 13: 566-571.
- Montgomery EA, Devanev KO, Giordano TJ, Weiss SW (1998) Inflammatory myxohyaline tumor of distal extremities with virocyte or Reed-Sternberg-like cells: a distinctive lesion with features simulating inflammatory conditions, Hodgkin's disease, and various sarcomas. Mod Pathol 11: 384-391. [Crossref]
- Meis JM, Kindblom LG, Mertens F (2013) Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma. In: Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F, eds. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. 4th ed. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer: 87–88.
2021 Copyright OAT. All rights reserv
Article Type
Image Article
Publication history
Received date: May 03, 2017
Accepted date: May 16, 2017
Published date: May 19, 2017
Copyright
© 2017 Fellner FA. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation
Fellner FA, Fellner CM, Scala M (2017) Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma of the wrist. Glob Imaging Insights 2: DOI: 10.15761/GII.1000120
Corresponding author
Franz A. Fellner
Central Radiology Institute, Kepler University Hospital, Medical Faculty of the Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria, Medical Faculty of the Friedrich-Alexander-University of Erlangen Nürnberg, Germany
E-mail : bhuvaneswari.bibleraaj@uhsm.nhs.uk

Figure 1. MR examination of the left wrist. a) PD-weighted fat suppressed, b) T1-weighted turbo spin-echo, and c) gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted turbo spin-echo with fat suppression in coronal orientation show a fairly demarcated, significantly gadolinium enhancing soft tissue mass located at the dorsal side of the wrist.

Figure 2. Sagittal PD-weighted fat suppressed (a) and transverse gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted turbo spin-echo with fat suppression demonstrate that the mass surrounds extensor tendons.


