A comprehensive subjective and objective physical examination was performed. Right shoulder active range of motion was significant for poor quality of shoulder flexion which deviated into scaption and an inability to actively abduct past 80 degrees. Passive range of motion was full, but the patient experienced his worst pain with end range internal rotation and mild posterior shoulder pain at end range adduction. Manual muscle testing was significant for 4-/5 weakness of right shoulder external rotation as well as weakness and pain with the empty can test. Palpation was performed for shoulder structures along with provocative tests, but the patient was not point tender to the acromioclavicular joint.
rotator cuff injuries, shoulder pain, diagnostic imaging, bone cysts, physical therapy modalities, radiography, humerus
A 51-year-old male was referred to Physical Therapy by his Family Nurse Practitioner with right anterior shoulder pain. Onset was 8 weeks prior after a fall while playing rugby. Pain was aggravated by reaching overhead and was reduced in a dependent position. No red flags were present.
A comprehensive subjective and objective physical examination was performed. Right shoulder active range of motion was significant for poor quality of shoulder flexion which deviated into scaption and an inability to actively abduct past 80 degrees. Passive range of motion was full, but the patient experienced his worst pain with end range internal rotation and mild posterior shoulder pain at end range adduction. Manual muscle testing was significant for 4-/5 weakness of right shoulder external rotation as well as weakness and pain with the empty can test. Palpation was performed for shoulder structures along with provocative tests, but the patient was not point tender to the acromioclavicular joint.
Radiographs can often show bony changes secondary to soft tissue pathology (Figure 1) [1]. Due to objective exam findings consistent with a full-thickness supraspinatus tear as well as the radiographic findings, the physical therapist ordered Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) which showed a full thickness tear of the supraspinatus tendon (Figure 2).
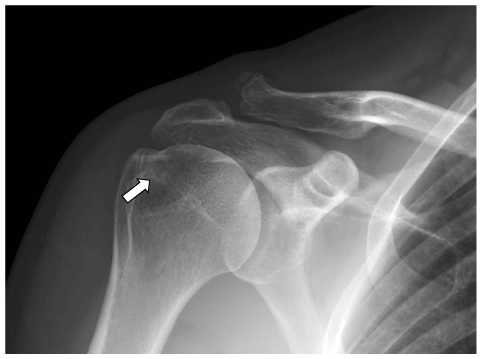
Figure 1. Anterior to Posterior projection right shoulder radiograph in external rotation (cropped) demonstrates a peripherally sclerotic rounded lucency projecting over the greater tuberosity consistent with subcortical cyst formation (white arrow). Also noted is moderate acromioclavicular osteoarthrosis
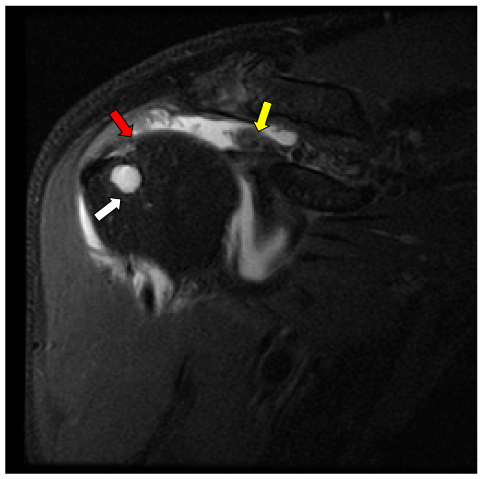
Figure 2. Coronal proton density fat saturated MRI sequence of the right shoulder demonstrates a large full-thickness tear of the supraspinatus tendon (distal tendon – red arrow) with retraction to the medial humeral head (retracted tendon - yellow arrow). Additionally, there is an associated rounded fluid signal lesion compatible with a subcortical cyst (white arrow) within the anterior greater tuberosity
Delaying surgical intervention after a traumatic rotator cuff tear has been associated with worse postoperative outcomes [2]. Plain radiographs can frequently show secondary signs of soft tissue pathology and are therefore the initial imaging modality of choice for almost all musculoskeletal conditions. In this case, prompt diagnosis through clinical examination with radiographic findings and confirmation via MRI allowed this patient to be directed to an orthopedic surgeon only 2 days after the initial physical therapy examination. The patient ultimately underwent a supraspinatus repair 3 months after the onset of symptoms and is expected to make a full recovery.
We affirm that we have no financial affiliation (including research funding) or involvement with any commercial organization that has a direct financial interest in any matter included in this manuscript. No other conflict of interest (i.e, personal associations or involvement as a director, officer, or expert witness) exists.
- Suluova F, Kanatli U, Ozturk BY, Esen E, Bolukbasi S (2014) Humeral head cysts: association with rotator cuff tears and age. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 24: 733-739. [Crossref]
- Petersen SA, Murphy TP (2011) The timing of rotator cuff repair for the restoration of function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20: 62-68. [Crossref]


