Abstract
Advanced breast cancer is an incurable disease. Goals of treatment are to prevent the progression of the disease and to maintain quality of life, limiting treatment related toxicity. First line systemic treatment choice is challenging. Many clinical trials have demonstrated safety and efficacy of metronomic chemotherapy.
To describe the exceptional long term complete response to metronomic chemotherapy in a patient with advanced breast cancer.
A 68-year-old woman presented in April 2019 with a painful and bleeding tumor mass in her right breast. The initial staging of the disease revealed lymph nodes and lung metastases. The decision of the multidisciplinary team was to initiate first line metronomic chemotherapy with vinorelbine and capecitabine.
A complete objective response in the breast and in the metastatic sites was reported after 3 months of treatment. No significant side effects were experienced.
Metronomic chemotherapy could be a valid treatment option in symptomatic metastatic breast cancer. Its low toxicity profile allows chronic administration and a prolonged control of the disease.
Keywords
metronomic chemotherapy, advanced breast cancer, local recurrence, complete response, low toxicity, tailoring therapies
Introduction
Metastatic breast cancer (MBC) is an incurable disease. Goals of treatment are to delay disease progression and to prolong survival while maintaining a good quality of life. Complete responses to treatments are rare in MBC and most patients have only temporary responses [1].
Metronomic chemotherapy (MC) is characterized by chronic administration of chemotherapy at low doses, with a frequent schedule of administration, at close and regular intervals and with no extended interruption. MC exerts both direct and indirect effects on tumor cells and on their microenvironment and causes less severe side effects than standard chemotherapy [2].
In MBC several studies have provided data on the clinical efficacy and low toxicity profile of metronomic chemotherapy [3-5].
Herein we report the case of a 68-year-old woman with breast cancer and associated synchronous lymph nodes and lung metastases who experienced exceptional long term complete response with low dose metronomic chemotherapy.
Clinical case
This is the case of a 68-year-old woman with family history of breast cancer presented in April 2019 with a painful and bleeding tumor mass in her right breast. Comorbidities were arterial hypertension and Paget's disease of the bone. Patient Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG- PS) was 2.
The vegetative and ulcerated lesion occupied the whole right breast. There was an additional satellite lesion of about 2 cm in the inner inferior quadrant of the right breast and enlarged lymph nodes measuring more than 1 cm in both the axilla (Figure 1).
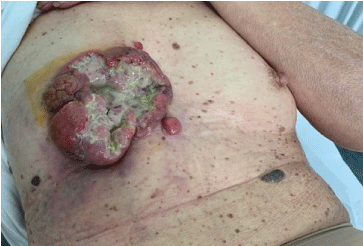
Figure 1. Right breast at baseline: vegetative and ulcerated tumor mass with an additional satellite lesion of about 2 cm in the inner inferior quadrant of the right breast
The left mammography did not show other lesions in the left breast, whereas the ultrasound confirmed bilateral axillary involvement.
The histopathological analysis of the punch biopsy of the breast mass showed an invasive ductal carcinoma, poorly differentiated (G3). Immunohistochemical exam revealed a luminal B-like staining; estrogen receptor 15%; progesterone receptor 5%; Ki-67 was at 45%. Her2/neu immunohistochemical status was 2+ using the DAKO HercepTest . Fluorescence in situ hybridization was negative.
The initial staging was performed using CT and bone scan.
The total body CT scan showed expansive tissue in the right breast of 9x4 cm. The tissue infiltrated the muscle fascia; a diffuse thickening of the surrounding skin coexisted. Right axillary lymph nodes with maximum diameter of 30 mm were detected in both the axilla, the largest in the right axillary area of 30x18 mm.
Multiple thoracic lymph nodes along the internal mammary chains were also identified.
In both lungs some nodules with random distribution were detected with maximum diameter of 20 mm.
The bone scan showed irregular hyperfixation to the middle third and distal middle third of the right tibial shaft and to the proximal third of the ipsilateral tibial shaft, to be referred to the pagetic disease.
The final stage was IV - cT4N1M1 (lung, lymph nodes) according to the 2019 AJCC Cancer Staging.
Laboratory tests revealed moderate anemia.
The decision of the multidisciplinary team was to initiate first line chemotherapy adapted to the patient's ECOG- PS. Endocrine treatment was excluded as it was necessary to obtain a rapid objective response to reduce patient-reported symptoms (pain and bleeding). Palliative surgical treatment was also excluded due to the breast mass extension.
Therefore, in June 2019, after discussing treatment options with the patient, metronomic chemotherapy was started with vinorelbine 40 mg each alternative day of the week (monday, wednesday and friday) and capecitabine 500 mg three times a day after meals, given continuously without drug-free periods [5].
Gradual regression of the tumor mass in the right breast and in the axillary lymph nodes was noted after two months of treatment. A complete objective response in the breast was reported after 4 months of treatment (Figure 2), as well as in the axilla and in the lung.
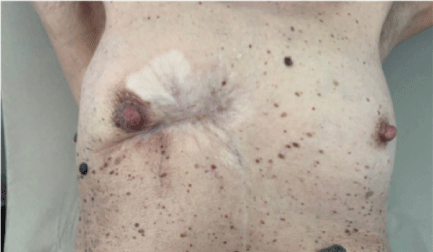
Figure 2. Complete objective response in the breast after 4 months of treatment with oral metronomic chemotherapy with vinorelbine and capecitabine
The patient was adherent and persistent to the metronomic treatment and no significant side effects were reported. She performed every month clinical examination and laboratory tests, whereas total body computed tomography scan was performed every four months.
In January 2022, after 20 months of metronomic chemotherapy the patients experienced right breast retroareolar pain. The CT scan showed right breast periareolar nodularity (diameter of 16 mm) that showed contrast enhancement and was surrounded by solid periwound tissue. There was retraction of the skin planes.
In consideration of the local recurrence of the disease, the metronomic treatment was suspended and a new chemotherapy regimen was started.
Discussion
Metastatic breast cancer is generally an incurable disease. The prognosis of patients with MBC is very poor and treatments are often palliative with limited goals.
Many options are currently available for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. The choice of systemic treatment represents a challenge for the medical oncologist today, especially in front line setting and in patients with endocrine positive disease.
Most efforts are aimed to tailor treatment strategies, taking into account the biological characteristics of the disease (ER, PGR, Her2 status, site and number of metastatic lesions), the characteristics of the patient (PS, comorbidities, preferences) and the characteristics of the systemic treatments (side effects, schedule of administration, efficacy).
In the absence of visceral crisis, endocrine agents ± CDK 4/6 inhibitors should be considered as the right option for the initial treatment of ER-positive, metastatic breast cancer due to their proven efficacy and favorable toxicity profile [6,7].. . However, some chemotherapy agents can induce higher response rates and more rapid responses, which are desirable effects in particular situations.
In the case we presented the choice of first line chemotherapy was motivated by the need to obtain a rapid response to treatment for the management of clinical symptoms mainly represented by bleeding and consequent anemia. Due to the patient's initial performance status (ECOG 2) and laboratory findings of moderate anemia, combination regimens such as e.g. anthracyclines and taxanes, were excluded because of their toxicity profile [8].
MC has shown efficacy in the three different breast cancer subtypes, luminal, Her2 positive and triple negative, with very low toxicity profile and high treatment tolerance [9].
In metastatic breast cancer, the majority of data on the use of different metronomic chemotherapy schedules comes from studies in pretreated patients.
Moreover, MC was recently proposed as a reasonable option of cancer treatment de-escalation during Covid 19 pandemic, due to its favorable safety profile [10].
Efficacy and safety of the all oral metronomic chemotherapy with vinorelbine and capecitabine have been explored in hormone receptor-positive/Her2-negative patients.
Initially, the phase I-II Victor-1 study [5] demonstrated a response rate of 16.1% and a CBR of 58.1% . Treatment schedule was vinorelbine given at the dose of 40 mg on days 1, 3 and 5, weekly combined with capecitabine 500 mg thrice daily continuously. Safety profile was good with only 9 total grade 3/4 adverse events reported, consisting primarily of hematologic events, neuropathy and hand-foot syndrome.
The subsequent confirmatory multicenter phase II Victor-2 study examined the same all oral combination of metronomic vinorelbine and capecitabine in MBC and reported a CBR of 80%, minimal grade 3/4 adverse events and no deterioration of quality of life [11].
Complete responses are rare in hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer [1].
In particular, long-lasting complete responses have been rarely reported with metronomic chemotherapy.
In our case, the choice of metronomic therapy allowed the patient to achieve an optimal and long lasting control of the disease locally and in the metastatic sites and to maintain the quality of life.
Conclusions
This clinical case demonstrated that all oral metronomic chemotherapy with vinorelbine plus capecitabine could be a valid treatment option in MBC. The low toxicity profile supports the chronic administration of the treatment, preserving the prognosis of breast cancer patients. Due to its safety and easy oral taking, this metronomic schema seems to be a good alternative treatment to more toxic combination schedules in particular in unfit patients.
Further ongoing prospective randomized studies will confirm more accurately where to place metronomic therapy in the therapeutic algorithm of metastatic breast cancer.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Acknowledgement
We thank Mr Antonio Guadalupi for his assistance with the manuscript.
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Figures 1 and 2.
References
- Galli G, Tessari A, Porcu L, Bregni G, Paolini B, et al. (2017) Complete remission in metastatic breast cancer: expecting the unexpected-results of a cross-sectional study. Breast Cancer 24: 635-41 [Crossref]
- Romiti A, Falcone R, Roberto M, Marchetti P (2017) Current achievements and future perspectives of metronomic chemotherapy. Invest New Drugs 35: 359-74. [Crossref]
- Fedele P, Marino A, Orlando L, Schiavone P, Nacci A, et al. (2012) Efficacy and safety of low-dose metronomic chemotherapy with capecitabine in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 48: 24-29. [Crossref]
- Stockler MR, Harvey VJ, Francis PA, Byrne MJ, Ackland SP, et al. (2011) Capecitabine versus classical cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil as first-line chemotherapy for advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29: 4498-504. [Crossref]
- Cazzaniga ME, Torri V, Villa F, Giuntini N, Riva F, et al. (2014) Efficacy and Safety of the All-Oral Schedule of Metronomic Vinorelbine and Capecitabine in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients: The Phase I-II VICTOR-1 Study. Int J Breast Cancer 2014: 769790 [Crossref]
- Tripathy D, Im SA, Colleoni M, Franke F, Bardia A, et al. (2018) Ribociclib plus endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer (MONALEESA-7): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 19: 904-915. [Crossref]
- Spring LM, Wander SA, Zangardi M, Bardia A (2019) CDK 4/6 Inhibitors in Breast Cancer: Current Controversies and Future Directions. Curr Oncol Rep 21: 25 [Crossref]
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Burzykowski T, Buyse M, Sledge G, Carmichael J, et al. (2008) Taxanes alone or in combination with anthracyclines as first-line therapy of patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 26: 1980-1986. [Crossref]
- Munzone E, Colleoni M (2015) Clinical overview of metronomic chemotherapy in breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 12: 631-644. [Crossref]
- Fedele P, Sanna V, Ancella A, Marino A, Calvani N, et al. (2021) De-escalating cancer treatments during COVID 19 pandemic: Is metronomic chemotherapy a reasonable option? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 157: 103148. [Crossref]
- Cazzaniga ME, Cortesi L, Ferzi A, Scaltriti L, Cicchiello F, et al. (2016) Metronomic chemotherapy with oral vinorelbine (mVNR) and capecitabine (mCAPE) in advanced HER2-negative breast cancer patients: is it a way to optimize disease control? Final results of the VICTOR-2 study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 160: 501-509. [Crossref]


