Background : Coronary anomalies are the causes of sudden cardiac deaths in young peoples, but usually asymptomatic. We perform this retrospective study to determine the types and prevalence of Coronary Anomalies of origin and course.
Method : The data of 9572 patients with Coronary CT-angiography by MDCT 640 Aquilion Toshiba machine were analysed.
Results : Anomalous origin and course of coronary artery were detected in 47 (0.49 %) of 9572 patients. The anomalous origins of Circumflex Artery from the RCA or the right sinus of Valsalva are most frequently visualized (15 pts [31.9%]). High taking off of RCA observed in 11 pts (23.4%).The RCA rising from the left sinus of Valsalva were seen in 8 pts (17%).The Left Coronary Artery originates from the right sinus of Valsalva in 5 pts (10,6%).The RCA arising from the LAD in 2pts (4,2%).Absent RCA in 2 case (4.2%) and single coronary artery from LSV in one case (2.1%). The LCA rising from the Pulmonary Artery (ALCAPA) in 2 cases and The RCA originating from the PA in one case (RCAPA).
Conclusion : Anomalies of coronary artery origin and course are rare but the diagnosis is very important to prevent SCD in young patients. MDCT with the Volume Rendered Images is the non-invasive modality that provides the valuable information to detect these anomalies.
Multidetector Computed Tomography, Anomalies of coronary origin and course, sinus of Valsalva
Coronary artery anomalies are a diverse group of congenital heart diseases with manifestations and pathological mechanisms are highly variable. Coronary anomalies include anomalies of origin and course, anomalies of intrinsic coronary arterial anatomy like myocardial bridge, anatomy of coronary termination as coronary artery fistula and anomalous anastomotic vessels. Anomalies of coronary origin and course may associate with arrhythmias, myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac deaths in young people, especially on effort like athletes. We study 9572 patients with coronary MDCT-angiography to evaluate the type and the incidence of coronary anomalies of origin and course.
All patients who underwent coronary CT-angiography by MDCT 64O Aquilion Toshiba equipment (IV contrast medium, gantry rotation of 0.33 msec, slice thickness 0.5mm) in MEDIC HCMC Viet Nam, from January 2016 to January 2019 were included. The main indications of CT-angiography were acute coronary syndrome, stable angina, coronary CT-angiography prior to surgery, congenital heart diseases involving coronary artery [1,2]
The CT-angiograms with coronary anomalies were selected and analysed. The anomalies of coronary origin and course were assessed [3,4].
We included 9572 pts with anomalies of coronary origin and course based on results of CT-angiograms that were interpreted by two cardiologists. Anomalous origin and course of coronary artery were detected in 47 (0.49 %) of 9572 patients. The mean age of these pts was 63± 8.4, M/F=1.8.
The anomalous origins of Circumflex Artery from the RCA or the right sinus of Valsalva are most frequently visualized (15 pts [31.9%]).High taking off of RCA observed in 11 pts (23.4%) The RCA rising from the left sinus of Valsalva were seen in 8 pts (17%).The Left Coronary Artery originates from the right sinus of Valsalva in 5 pts (10.6%), in this subgroup, a patient presented by myocardial infarction resulting cardiac arrest was notified, the surgical re-implantation of LCA was performed .The RCA arising from the LAD in 2pts (4,2%). Absent RCA in 2 case (4.2%) and single coronary artery from LSV in one case (2.1%). The Left Coronary Artery arising from the Pulmonary Artery (ALCAPA) in 2 cases (4.2%) and The RCA originating from the PA (RCAPA) in one case (2.1%) (Table 1)
Table 1. RSV: Right sinus of Valsalva, LSV: Left sinus of Valsalva, ALCAPA: Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from The Pulmonary Artery, RCAPA: Anomalous Origin of the Right Coronary Artery off The Pulmonary Artery.
Type of coronary anomaly |
n |
Anomaly Prevalence |
Prevalence among all pts |
Cx originating fr. RCA/RSV |
15 |
31.9% |
0.16% |
High taking off of RCA |
11 |
23.4% |
0.11% |
RCA rising from LSV |
8 |
17% |
0.084% |
LCA rising from the RSV |
5 |
10.6% |
0.052% |
RCA arising from LAD |
2 |
4.2% |
0.021% |
Absent RCA |
2 |
4.2% |
0.021% |
Single coronary artery fr. LSV |
1 |
2.1% |
0.01% |
ALCAPA |
2 |
4.2% |
0.021% |
RCAPA |
1 |
2.1% |
0.01% |
This patient is of 52 ages, presented by atypical chest pain, the single coronary artery originating from LSV. The other case report of Panduranga, et al. [5] revealed the single coronary artery arising from RSV with exertional angina (Figure 1) [6,7].
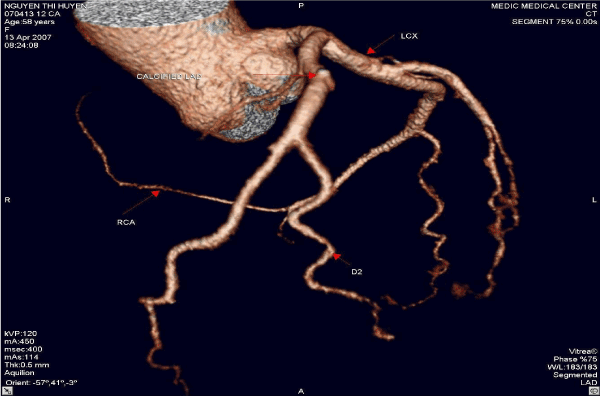
Figure 1. Single coronary artery rising from LSV.
We have in our study one young patient of 24 years old that had been transferred to the hospital by cardiac arrest, related to this anomaly. Operative re-implanted had been indicated to save the patient (Figures 2-10).
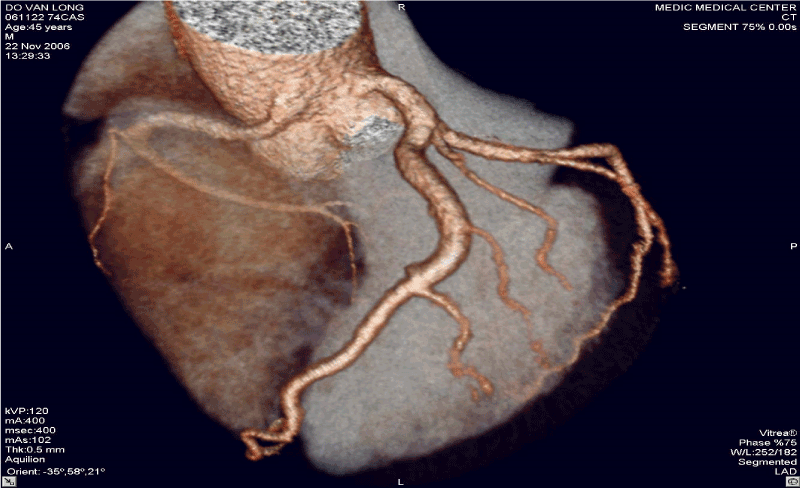
Figure 2. High taking off of RCA, some time causes myocardial infarction due to excessive angulation between RCA and Aorta.
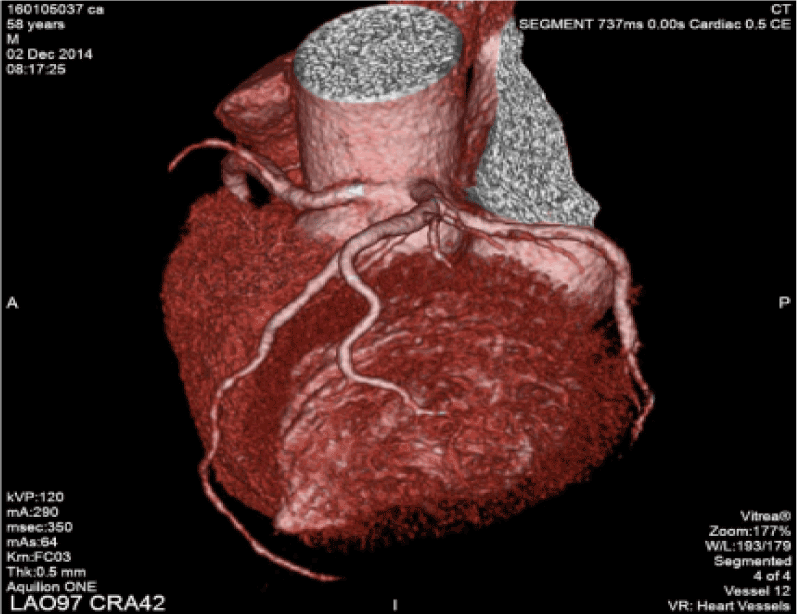
Figure 3. RCA originates from LSV with intra-arterial course resulting Angina.
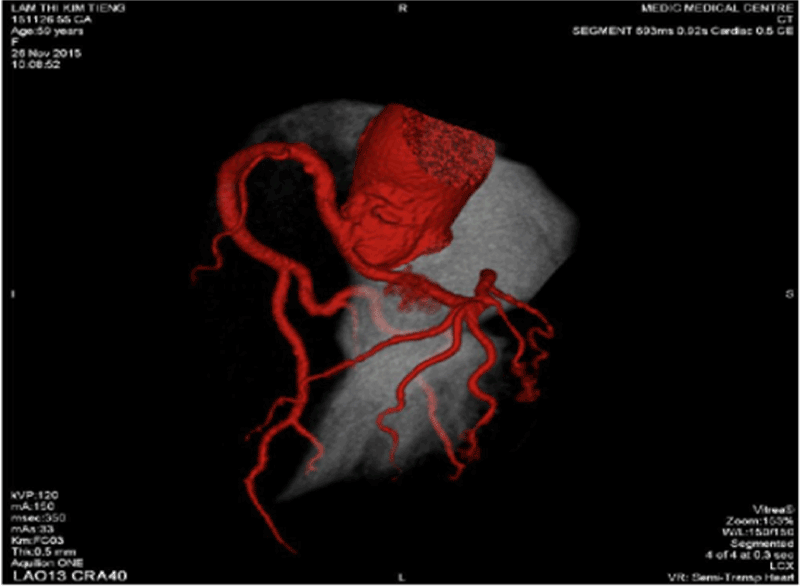
Figure 4. Anomalous origin of LCA from RSV
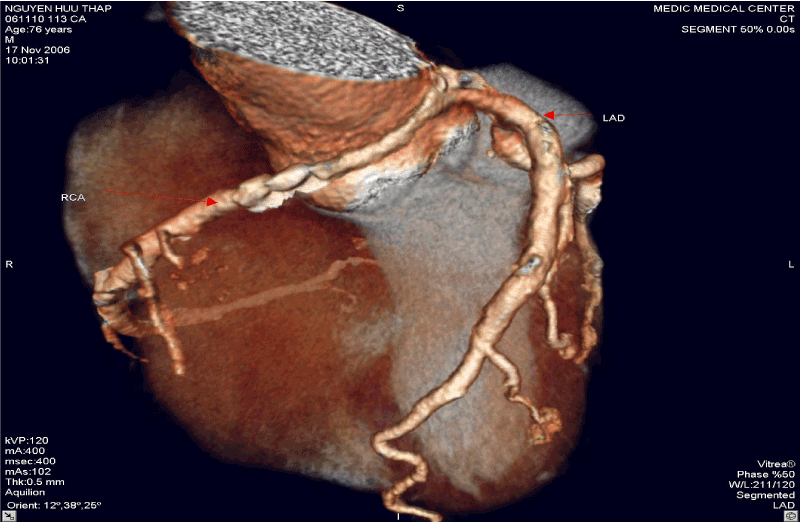
Figure 5. RCA rising from LSV and Intra-arterial course of RCA
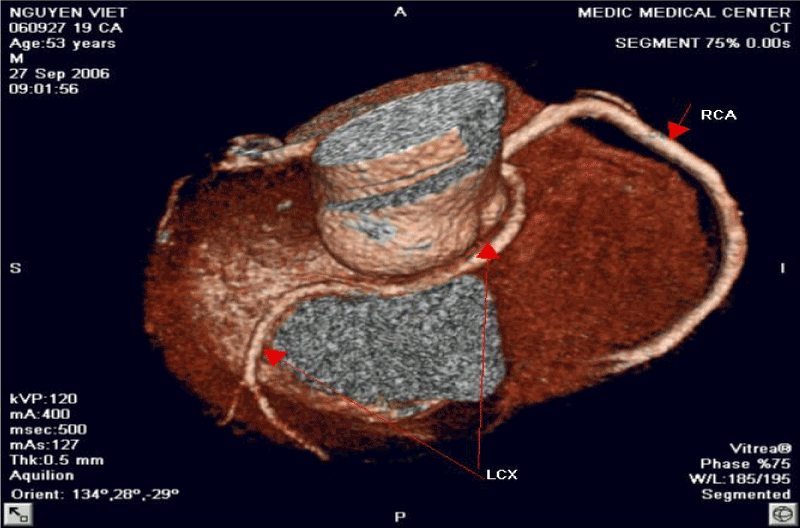
Figure 6. LCx arising from the RSV and Retro Aortic Course of LCx
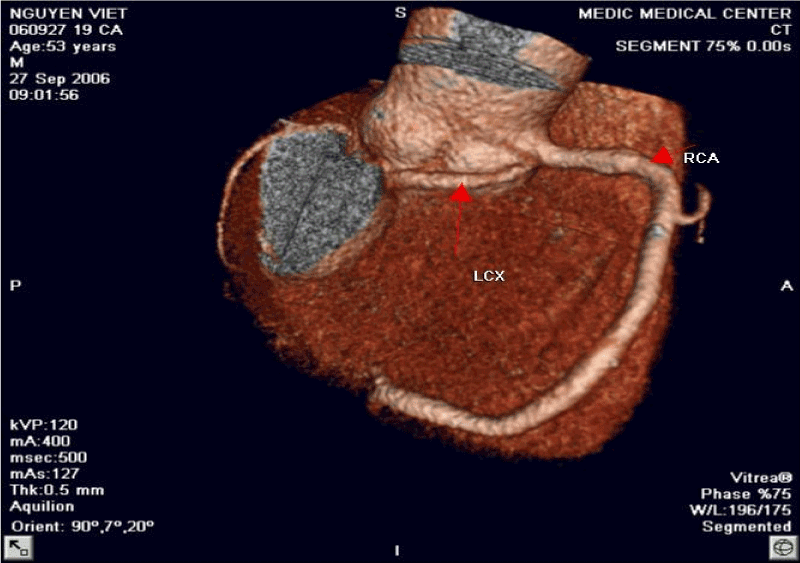
Figure 7. LCx arising from the RSV and Retro Aortic Course of LCx
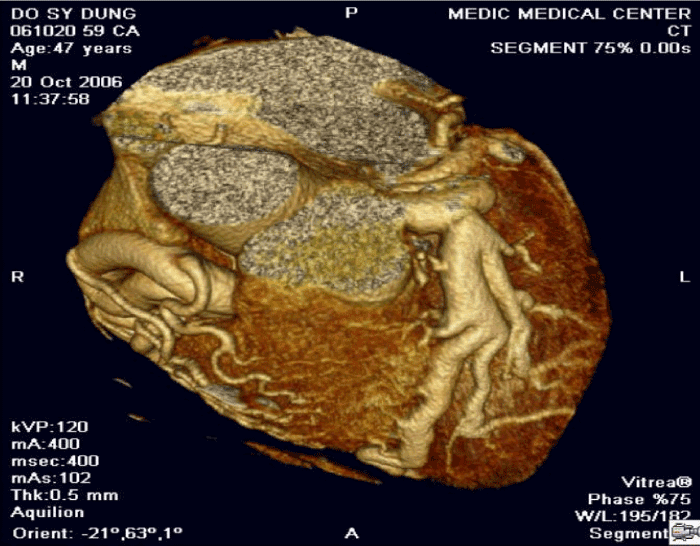
Figure 8. Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from The Pulmonary Artery
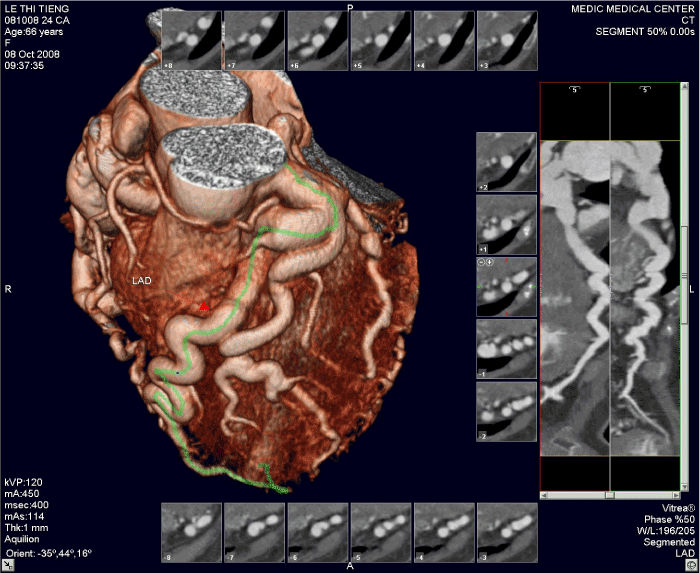
Figure 9. Other case of ALCAPA.
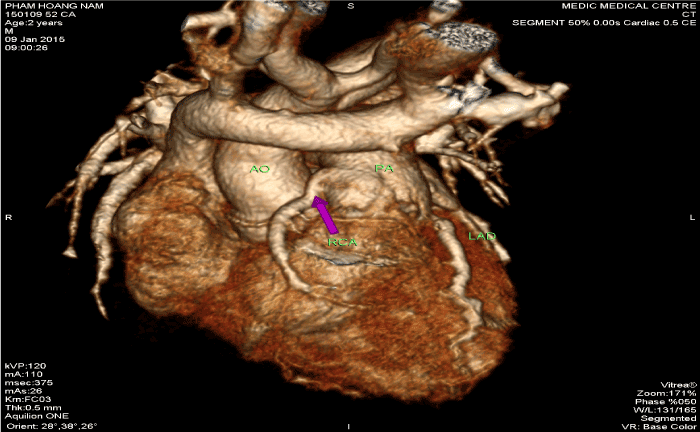
Figure 10. Anomalous Origin of the Right Coronary Artery off The Pulmonary Artery
In our study, coronary anomalies of origin and course were detected in 47 of 9572 patients (0,49%) that is consistent with the incidence of 0.27% to 1.66% reported in other series. The most frequent anomaly of origin and course was the Cx Artery arising from RCA/RSV (31.9% of anomaly prevalence and 0.16% among all patients), this incidence is lower than previous published studies.
The anomalies of origin and course of RCA were found in 17% and 4.2% respectively from LSV and LAD. This incidence is lower in comparison with previous study.
Sudden deaths, myocardial infarction, arrhythmias related to the coronary anomalies were reported previously. But these anomalies often asymptomatic, so early detection of coronary anomalies of origin and course is highly important.
The former studies mainly based on the result of coronary angiography that is invasive modality. This study demonstrates MDCT is the noninvasive modality that provides important information related to coronary anatomy. Currently MDCT and MRI become fundamental to detection and diagnosis of coronary anomalies.
Contrast enhanced ECG-gated 640-row MDCT coronary angiography is an accurate diagnostic method that can precisely detect the coronary anomalies of origin and course.
- Dodd JD, Ferencik M, Liberthson RR, Cury RC, Hoffmann U, et al. (2007) Congenital anomalies of coronary artery origin in adults: 64-MDCT appearance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188: W138-146. [crossref]
- Hoffman JI, Kaplan S, Liberthson RR (2004) Prevalence of congenital heart disease. Am Heart J 147: 425-439. [crossref]
- Stuart J Hutchison, Naeem Merchant (2015) Principles of cardiac and vascular computed tomography. Elsevier.
- Lee HJ (2012) Anomalous Origin of the Right Coronary Artery from the Left Coronary Sinus with an interarterial course: Subtypes and Clinical Importance. Radiology 262.
- Panduranga P, Riyami AA (2016) Single Coronary Artery from right aortic sinus in a very elderly patient.
- Prasad S, Vijayakumar DH ( 2017 ) Detection of Coronary Artery Anomalies Using 64 slice MDCT Angiography. Int J Contemporary Med Sur Rad 2: 75-79.
- Yuksel S ( 2013 ) The primary anomalies of coronary artery origin and course: A coronary angiographic analysis of 16,573 patients. Clin Cardiol 18:121-123.










