Cancer is one of the major causes of human death worldwide. The death caused by cancer mainly is lung cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer, carcinoma of colon and rectum. It is estimated that about 1,688,780 new cancer cases will be diagnosed in the United States in 2017 and 600,920 cancer cases are expected to die, which is about 1,650 people per day. For all sites combined, the cancer incidence rate is 20% higher in men than in women, while the cancer death rate is 40% higher [1]. It has been reported that 4,292,000 new cancer cases and 2,814,000 cancer deaths occurred in 2015 in China, with lung cancer being the most common incident cancer and the leading cause of cancer death. Stomach, esophageal, and liver cancers were also commonly diagnosed and were identified as leading causes of cancer death [2]. Thus, it is urgent to develop novel anticancer agents, especially find the novel anticancer agents from Chinese traditional plant medicines, for many kinds of Chinese traditional plant medicines have ever been used in clinical for treatment cancer.
The Roots of Radix Actinidia chinensis has been reported to exhibit a wide spectrum of anticancer activity against several cancer cell lines [3]. In current work, we obtained five different polar extractions (Ethylacetate extraction, Trichloromethane extraction, Dichloromethane extraction, Methanol extraction and water extraction) from the roots of Radix Actinidia chinensis (Figure 1). The obtained five extractions were preliminarily evaluated for their cytotoxicity towards A549, HCT116 and MCF-7 cell lines [4-6] (Table 1). The results showed that the ethyl acetate extraction and dichloromethane extraction are the more potent extractions among them, which provide the guidance for the further research.
Table 1. The cytotoxicity of different extractions towards A549, HCT116 and MCF-7 cell lines at 50μg/mL
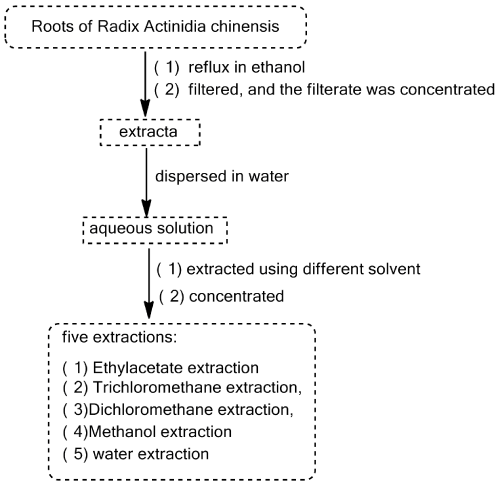
Figure 1. The processes of extractions of the Roots of Radix Actinidia chinensis
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the College Students' innovation and entrepreneurship training project (201710389067).
References
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2017) Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67: 7-30. [Crossref]
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, et al. (2016) Cancer Statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66: 115-132. [Crossref]
- Li J, Xu Y, Yang XD, Liu Y, Luan YT, et al. (2017) Effects of Kiwi Root Antitumor and Its Progress in Clinical Research. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine 35: 2745-2747.
- Yong JP, Lu CZ, Wu X (2015) Potential anticancer agents I. synthesis of isoxazole moiety containing quinazoline derivatives and preliminarily in vitro anticancer activity. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 15: 131-136. [Crossref]
- Yong J, Lu C, Wu X (2015) Synthesis and biological evaluation of quinazoline derivatives as potential anticancer agents (II). Anticancer agents Med Chem 15: 1326-1332. [Crossref]
- Yong J, Lu C, Wu X (2014) Synthesis of Isoxazole Moiety Containing Ferrocene Derivatives and Preliminarily in vitro Anticancer Activity. Med Chem Comm 5: 968-972.

