Evinacumab, being a fully humanized anti-ANGPTL3 monoclonal antibody, February, 11th, 2021, as Evkeeza® preparation, has been registered by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration for the treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia (HoHF).
Angiopoietin-like proteins (ANGPTL) include the compounds ANGPTL1 through ANGPTL8 and belong to the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family.
ANGPTL3, ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 play an important role in terms of cardiovascular physiology and lipid metabolism. These proteins regulate the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins [1,2]. The main source of ANGPTL3 is liver, ANGPTL4 is liver, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, gut, heart and brain, and ANGPTL8 is liver and adipose tissue. These proteins form a ANGPTL3-4-8 system that controls the availability of triglycerides depending on the current nutritional status of the body, temperature and physical activity (Figure 1) [1,2].
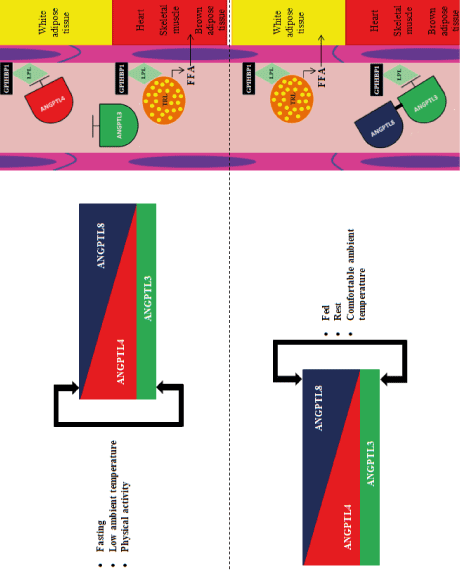
Figure 1: ANGPTL3-4-8 system mechanism of action in the regulation of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism [1-3]. ANGPTL3 – angiopoetin-like protein 3; ANGPTL4 - angiopoetin-like protein 4; ANGPTL8 - angiopoetin-like protein 8; TLR - triglyceride-rich lipoprotein; FFA - free fatty acids; GPIHBP1 - glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchored high density lipoprotein binding protein 1; LPL - lipoprotein lipase
Within white adipose tissue, LPL activity during fasting is reduced by ANGPTL4. In the heart, skeletal muscle and brown adipose tissue, the activity of LPL after a meal is reduced by ANGPTL3 and ANGPTL8 (after a meal, the expression of ANGPTL8 is particularly increased, while the expression of ANGPTL3 is not dependent on the nutritional status) forming a heterodimer (ANGPTL8 is an activator of ANGPTL3 (Figure 1). Thus, the ANGPTL3-4-8 system plays an important role in regulating triglyceride metabolism [1-3].
In a study by Dewey et al. it was found that persons carrying the LOF mutation (loss of function) of the Angptl3 gene were characterized by decreased plasma concentrations of the four major lipid fractions, which translated into a 39% reduction in the risk of ischemic heart disease in these patients [4].
Taking into account the important role of ANGPTL3 in lipid metabolism and the beneficial cardiovascular effects of the reduced activity of this protein, it resulted in the development of a drug that is a human anti-ANGPTL3 monoclonal antibody – evinacumab (RENG1500).
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study, Raal et al. assessed the therapeutic efficacy of evinacumab in 65 patients with HoHF. The subjects were administered evinacumab intravenously at a dose of 15 mg / kg. every 4 weeks or placebo. The mean baseline plasma LDL concentration was 255 mg/dl despite intensive lipid lowering treatment. After 24 weeks, a significant improvement in lipid parameters was demonstrated (Table 1) [5].
Table 1: Changes in lipid parameters during treatment with evinacumab. Adapted from Raal F. et al. [5].
The results of clinical trials also indicate the beneficial effects of evinacumab in the treatment of resistant hypercholesterolaemia, heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia and severe hypertriglyceridaemia [6-8].
The future of evinacumab seems a little different than other drugs dedicated for severe hypercholesterolemia, like PCSK9 inhibitors (alirocumab, evolocumab) or PCSK9 small interfering RNA particles (inclisiran). The last two do not address hypertriglyceridemia. Thus evinacumab would be the drug of choice together with statin, as the remedy for mixed hyperlipidemia in very high risk and extremally high cardiovascular risk patients. It might be the helpful tool for some of atherogenic dyslipidemia cases. New clinical trials, however, are needed for broadening our experiences in combining evinacumab with ezetimibe, bempedoic acid or even with PCSK9 drugs in patients now treated with LDL-apheresis.
- Surma S, Romańczyk M, Filipiak KJ (2021) Angiopoietin-like proteins inhibitors: new horizons in the treatment of atherogenic dyslipidemia and familial hypercholesterolemia. Cardiol J. [Crossref]
- Surma S, Romańczyk M. Filipiak KJ (2021) Evinacumab — an ANGPTL3 inhibitor; a new drug in the treatment of lipid disorders. Review on the literature and clinical studies. Folia Cardiol 16: 30-39.
- Zhang R (2016) The ANGPTL3-4-8 model, a molecular mechanism for triglyceride trafficking. Open Biol 6: 150272. [Crossref]
- Dewey F, Gusarova V, Dunbar R, et al. (2017) Genetic and pharmacologic inactivation of ANGPTL3 and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 377: 211-221. [Crossref]
- Raal FJ, Rosenson RS, Reeskamp LF, Hovingh GK, Kastelein JJP, et al. (2020) Evinacumab for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 383: 711-720. [Crossref]
- Rosenson RS, Burgess LJ, Ebenbichler CF, Baum SJ, Stroes ESG, et al. (2020) Evinacumab in patients with refractory hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 383: 2307-2319. [Crossref]
- Ahmad Z, Banerjee P, Hamon S, Chan KC, Bouzelmat A, et al. (2019) Inhibition of angiopoietin-like protein 3 with a monoclonal antibody reduces triglycerides in hypertriglyceridemia. Circulation 140: 470-486. [Crossref]
- Rosenson RS (2021) A phase 2 trial of the efficacy and safety of evinacumab in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia. American College of Cardiology's 70th Annual Scientific Session & Expo; May 15 – 17, 2021.

